Setting up a new repository
How do I Join the Maintainers Team?
- Sign up for opensauced.pizza
- Join discord.
- Prove your pizza worth!
Requirements
For the purpose of this tutorial, our target demo repository will be called open-sauced/npx-check-engines.
The steps described here mirror open-sauced/check-engines.
The octoherd scripts assume you have exported a programatic token similar to:
export GH_TOKEN="ghp_Q8TZZT9ypgqw3EeABoCWPcwZBHpjZJ9hI42n"
Creating a new repo
Don't spend too much time thinking of a name or a catchy description, just set license to MIT and rocket jump!
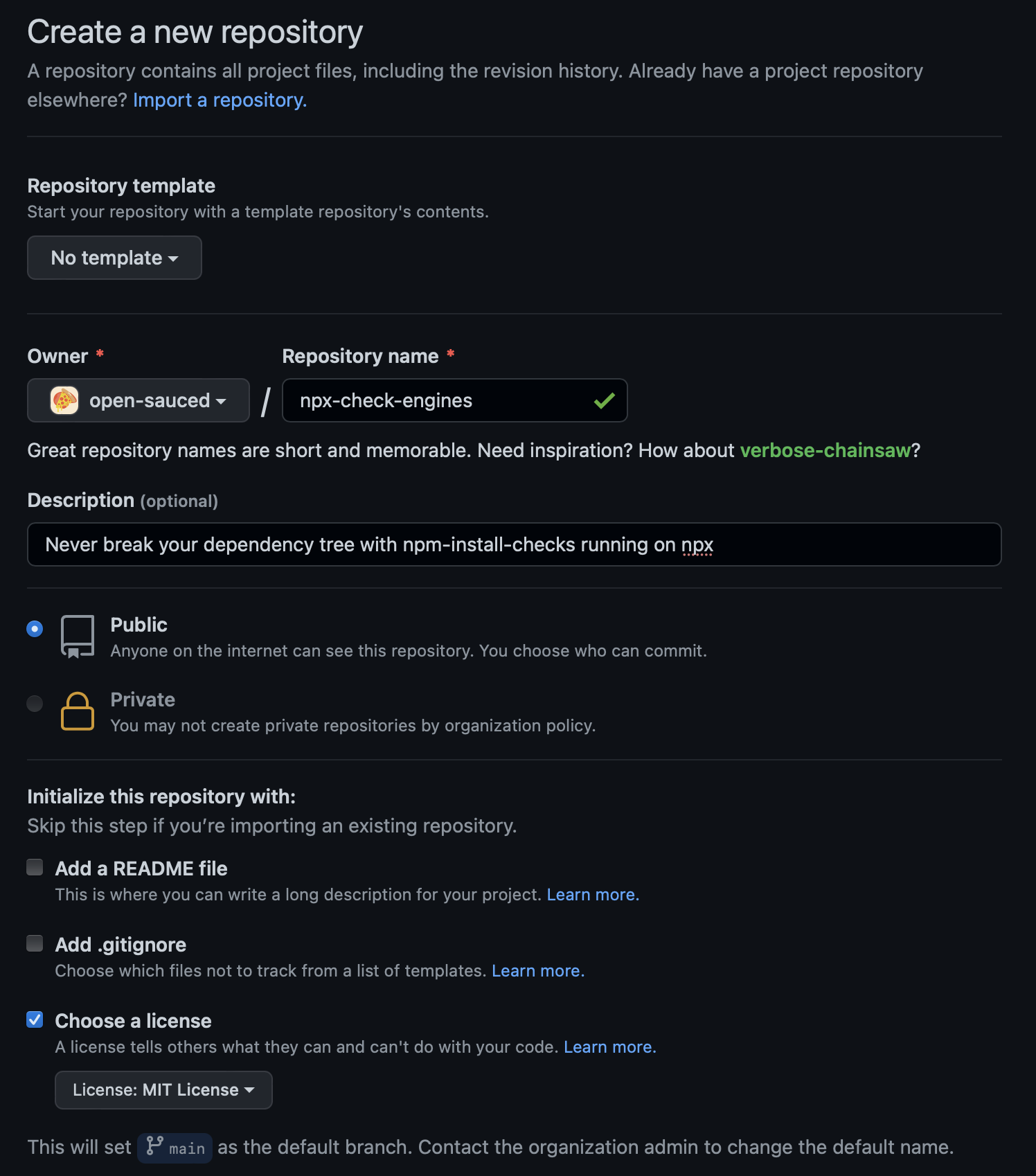
Syncing settings with opensauced.pizza
Squashing pull requests is the minimum requirement but the other options are quite useful at various stages of development.
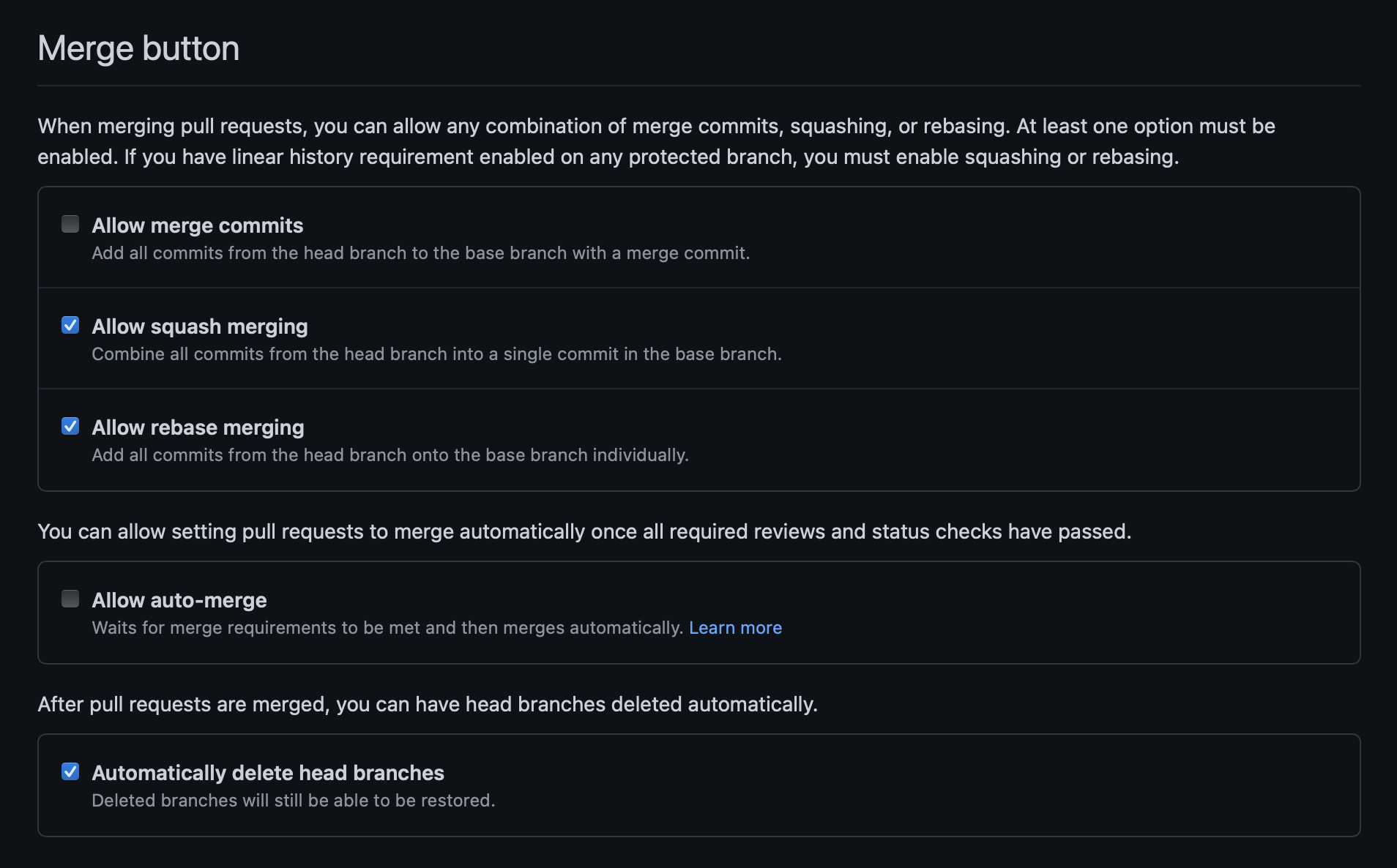
Copy most of the relevant settings with:
npx octoherd-script-sync-repo-settings \
--template "open-sauced/open-sauced" \
-T $GH_TOKEN \
-R "open-sauced/check-engines"
Otherwise you can disable "Projects" and "Wikis" for the selected repository as we are handling them on a larger scale.
Syncing labels with opensauced.pizza
The default labels have some missing emojis. Copy the rest with:
npx octoherd-script-copy-labels \
--template "open-sauced/open-sauced" \
-T $GH_TOKEN \
-R "open-sauced/check-engines"
Then go back to your repository and delete:
- documentation
- 👀 needs-triage (green background one)
- other potential duplicates if the above race condition is different
Syncing branch protections with opensauced.pizza
This topic is more complex but in a sense tap the main branch and enable everything except "Restrict who can dismiss pull request reviews" and "Restrict who can push to matching branches" in the first section.
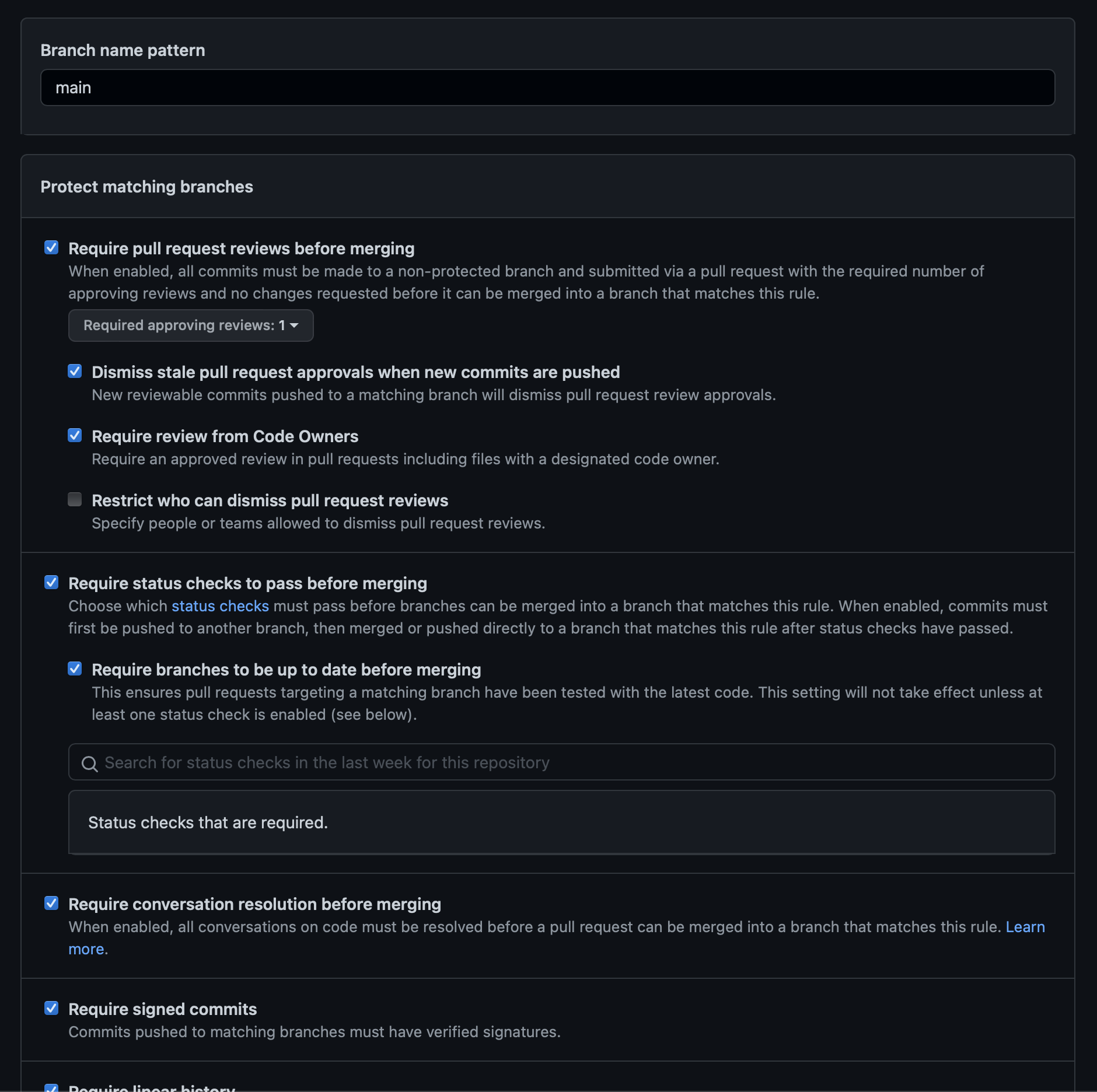
The "Rules applied to everyone including administrators" is more on an unused override.
Most of the time this process is super manual but in the limited cases where we need this run:
npx @octoherd/script-sync-branch-protections \
--template "open-sauced/open-sauced" \
-T $GH_TOKEN \
-R "open-sauced/check-engines"
Setting up workflows
Most collaborative projects require compliance flows powered by amannn/action-semantic-pull-request and actions/first-interaction.
Pull requests require triage powered by bdougie/take-action.
Most node projects will require release automation powered by @open-sauced/semantic-release-conventional-config.
Other development workflows are less common and opinionated towards decentralised collaboration. Use these as example backbones for your new repository.
Setting up environments and secrets
As you may have noticed in the previous step or in the actions visualisations, the release workflows enable named environments.
These have to be manually set up, along with their secrets and branch protections.
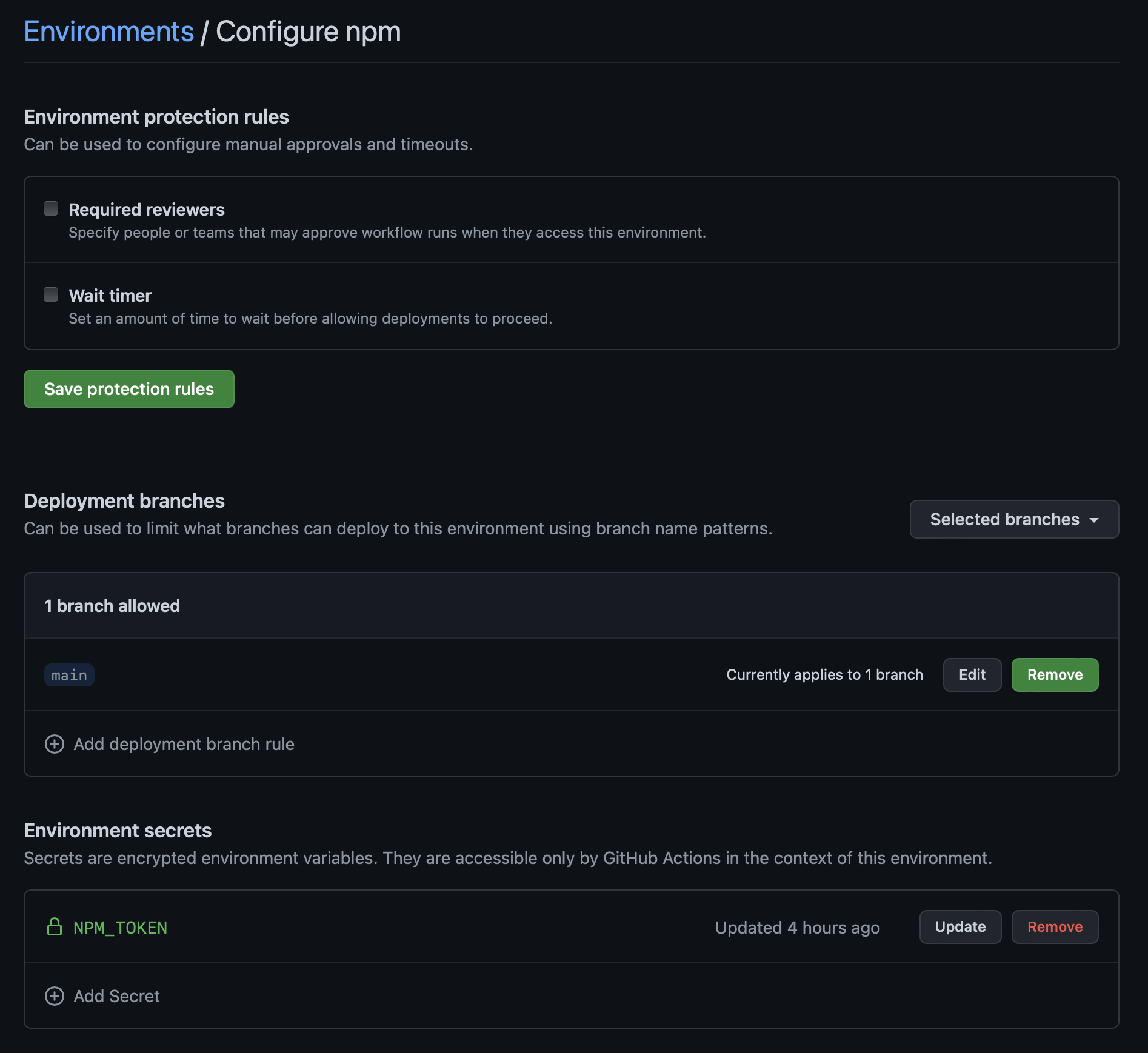
If using npm or ghcr it is likely you will add a couple variables here.